Connectivity Module¶
Overview¶
The Connectivity module for the Alexa Auto SDK creates a lower data consumption mode for Alexa, allowing automakers to offer tiered functionality based on the status of their connectivity plans. By using this module, you can send the customer's connectivity status from the vehicle to Alexa, which determines whether the customer can enjoy a full or partial set of Alexa features. This module allows the automaker to create tiered access to Alexa for customers and offer up-sell opportunities to subscribe to a full connectivity plan.
A customer who purchases an Alexa-enabled vehicle typically has to subscribe to the automaker’s connectivity plans and accept the automaker's and network provider's terms and conditions to access Alexa. Without the Connectivity module, if the customer declines the terms and conditions, or does not have a data plan (for example, due to plan expiration), the customer loses access to Alexa. The Connectivity module, however, provides an option that allows the automaker to offer a reduced set of Alexa functionality and limited bandwidth consumption for little or no cost. In this low data consumption mode, utterances sent to the cloud are filtered by feature, because the Connectivity module offers a restricted set of features. For example, when a user accesses Alexa through the Connectivity module, an utterance requesting music streaming does not start the streaming but turns on the FM radio station that was last played. Features such as weather and traffic remain accessible.
Your application's Connectivity module integration is responsible for:
- Providing the network identifier for Alexa to send to the mobile network operator (MNO)
- Providing the vehicle's connection properties and configurations to Alexa
Configuring the Connectivity Module¶
The Connectivity module does not require Engine configuration.
Using the Connectivity AASB Messages¶
Providing the Network Identifier¶
The network identifier is agnostic of the data plan and is assigned when initially integrated into the vehicle. It links the device with the network provider and enables the network provider to identify and provide device connectivity. Examples of the network identifier are the Embedded SIM ID (eSIM ID) and a globally unique ID (GUID). Which ID to use depends on the implementation determined in agreement with Amazon, OEM, and MNO.
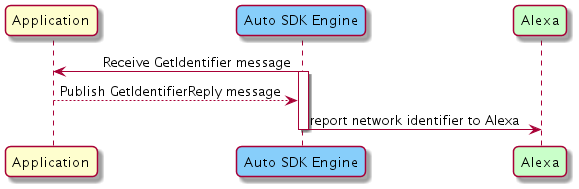
During device discovery the Engine publishes the GetIdentifier message. To report the network identifier to Alexa, publish the GetIdentifierReply message.
Click to expand or collapse sequence diagram: Providing the Network Identifier
Providing the Connectivity Status¶
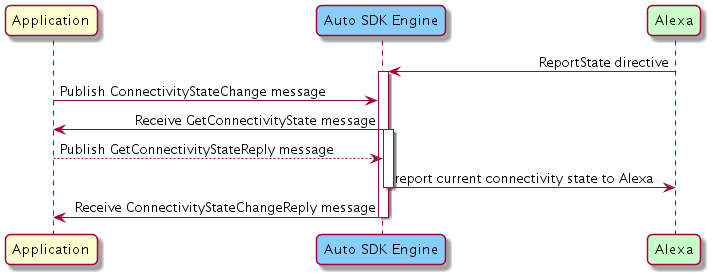
When a client application initiates connection with Alexa or when Alexa requests a report of the current connectivity state, publish the ConnectivityStateChange message. In response, the Engine will publish the GetConnectivityState message to which your application must publish the GetConnectivityStateReply message containing the connectivity state. The Engine will then publish the ConnectivityStateChangeReply message to indicate if the connectivity state was processed successfully.
Alexa parses the internet connectivity information from the vehicle and determines whether the customer is eligible for the full or partial Alexa experience. The connectivityState obtained in the GetConnectivityState reply payload has the following schema:
{
"managedProvider": {
"type": "{{STRING_ENUM}}",
"id": "{{STRING}}"
},
"termStatus": "{{STRING_ENUM}}",
"termsVersion": "{{STRING}}",
"dataPlan": {
"type": "{{STRING_ENUM}}",
"endDate": "{{STRING}}"
},
"dataPlansAvailable": ["{{STRING}}", "{{STRING}}", ...]
}
Click to expand or collapse details about the objects in the payload
| Property | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
dataPlan |
Object | It provides the active data plan type and end date. | Yes (only when managedProvider.type is MANAGED) |
dataPlan.type |
String | Accepted values:
PAID or TRIAL data plan has unrestricted access to all Alexa features. |
Yes |
dataPlan.endDate |
String | It specifies the date on which the trial data plan ends. If it is not set, there is no end date for the plan. The value is in the RFC 3339 format. | Yes (only when dataPlan.type is TRIAL) |
termsStatus |
String | It indicates whether the customer has accepted the terms and conditions of the OEM and MNO. If it is not set, the behavior is the same as when it is set to DECLINED. Accepted values:
|
No, but recommended |
termsVersion |
String | It indicates the version of the terms and conditions presented to the user. Do not use termsVersion if you do not use termsStatus. Maximum length is 250 characters. Note: If you implemented Auto SDK 3.1 with the Connectivity module, a default value is automatically assigned to termsVersion. For Auto SDK 3.2 or later, be sure to specify termsVersion. Otherwise, the MNO is not notified of the correct version of the terms and conditions presented to the user. |
Yes (only when termsStatus is provided) |
dataPlansAvailable |
String array | It indicates the data plans that can be activated. Accepted values are PAID, AMAZON_SPONSORED, and TRIAL. For example, if the array is ["TRIAL", "AMAZON_SPONSORED", "PAID"], Alexa encourages the user to upgrade from an AMAZON_SPONSORED plan to a TRIAL plan or from a TRIAL plan to a PAID plan. |
No |
managedProvider |
Object | It provides information about the type of network connectivity that the device has. | Yes |
managedProvider.type |
String | Accepted Values:
|
Yes |
managedProvider.id |
String | It specifies the name of the provider that manages connectivity. The only accepted value is AMAZON. |
Yes (only when managedProvider.type is MANAGED) |
Click to expand or collapse sequence diagram: Connectivity Report
Activating Voice Up-Sell Conversation¶
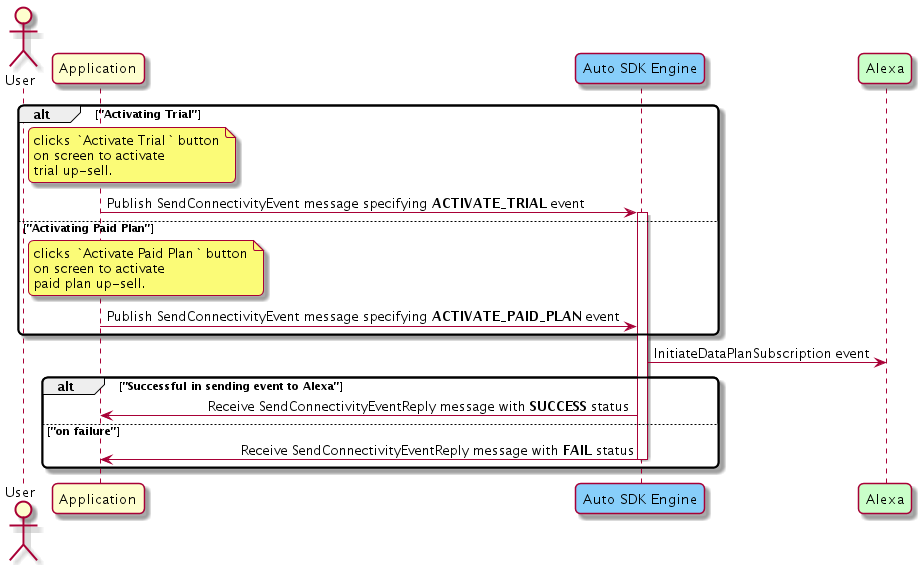
To activate the voice up-sell conversation with Alexa (e.g., to activate the trial or paid plan subscription), publish the SendConnectivityEvent message. The Engine publishes the SendConnectivityEventReply message specifying the delivery status of the event. The event sent in the SendConnectivityEvent message payload has the following schema:
{
"type": "{{STRING}}"
}
Note: Alexa requires the customer to have accepted the OEM and network provider's terms and conditions before starting the voice conversation.
Click to expand or collapse details about the objects in the payload
| Property | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
String | Represents the type of the connectivity event to Alexa. Accepted Values:
|
Yes |
Click to expand or collapse sequence diagram: Send Connectivity Event
Integrating the Connectivity Module Into Your Application¶
C++ MessageBroker Integration¶
Use the Engine's MessageBroker to publish "Connectivity" AASB messages and subscribe to their replies.
Click to expand or collapse C++ sample code
#include <AACE/Core/MessageBroker.h>
#include <AASB/Message/Connectivity/AlexaConnectivity/StatusCode.h>
#include <AASB/Message/Connectivity/AlexaConnectivity/ConnectivityStateChangeMessage.h>
#include <AASB/Message/Connectivity/AlexaConnectivity/GetConnectivityStateMessage.h>
#include <AASB/Message/Connectivity/AlexaConnectivity/GetIdentifierMessage.h>
#include <AASB/Message/Connectivity/AlexaConnectivity/SendConnectivityEventMessage.h>
#include <nlohmann/json.hpp>
using json = nlohmann::json;
class MyAlexaConnectivityHandler {
// Subscribe to messages from the Engine
void MyAlexaConnectivityHandler::subscribeToAASBMessages() {
m_messageBroker->subscribe(
[=](const std::string& message) { handleGetConnectivityStateMessage(message); },
GetConnectivityStateMessage::topic(),
GetConnectivityStateMessage::action());
m_messageBroker->subscribe(
[=](const std::string& message) { handleGetIdentifierMessage(message); },
GetIdentifierMessage::topic(),
GetIdentifierMessage::action());
m_messageBroker->subscribe(
[=](const std::string& message) { handleConnectivityStateChangeReplyMessage(message); },
ConnectivityStateChangeMessageReply::topic(),
ConnectivityStateChangeMessageReply::action());
m_messageBroker->subscribe(
[=](const std::string& message) { handleSendConnectivityEventReplyMessage(message); },
SendConnectivityEventMessageReply::topic(),
SendConnectivityEventMessageReply::action());
}
// Handle the ConnectivityStateChange reply message from the Engine
void MyAlexaConnectivityHandler::handleConnectivityStateChangeReplyMessage(const std::string& message) {
ConnectivityStateChangeMessageReply msg = json::parse(message);
std::string messageId = msg.header.messageDescription.replyToId;
// ...Handle change in the connectivity state...
}
// Handle the SendConnectivityEvent reply message from the Engine
void MyAlexaConnectivityHandler::handleSendConnectivityEventReplyMessage(const std::string& message) {
SendConnectivityEventMessageReply msg = json::parse(message);
std::string messageId = msg.header.messageDescription.replyToId;
StatusCode statusCode = msg.payload.statusCode;
// ...Handle delivery status of the event...
}
// Handle the GetConnectivityState message from the Engine and publish the reply message to the Engine
void MyAlexaConnectivityHandler::handleGetConnectivityStateMessage(const std::string& message) {
GetConnectivityStateMessage msg = json::parse(message);
GetConnectivityStateMessageReply replyMsg;
replyMsg.header.messageDescription.replyToId = msg.header.id;
replyMsg.payload.connectivityState = getConnectivityState();
m_messageBroker->publish(replyMsg.toString());
}
// Handle the GetIdentifier message from the Engine and publish the reply message to the Engine
void MyAlexaConnectivityHandler::handleGetIdentifierMessage(const std::string& message) {
GetIdentifierMessage msg = json::parse(message);
GetIdentifierMessageReply replyMsg;
replyMsg.header.messageDescription.replyToId = msg.header.id;
replyMsg.payload.identifier = getIdentifier();
m_messageBroker->publish(replyMsg.toString());
}
// To report a connectivity status change to Alexa, publish a ConnectivityStateChange message to the Engine
bool MyAlexaConnectivityHandler::connectivityStateChange() {
ConnectivityStateChangeMessage msg;
m_messageBroker->publish(msg.toString());
// The Engine will send the ConnectivityStateChangeReply message
// Return the success status from reply message payload
}
// To activate a voice up-sell conversation with Alexa, publish a SendConnectivityEvent message to the Engine
StatusCode MyAlexaConnectivityHandler::sendConnectivityEvent(const std::string& event) {
SendConnectivityEventMessage msg;
msg.payload.event = event;
m_messageBroker->publish(msg.toString());
// The Engine will send the SendConnectivityEventReply message
// Return the statusCode from reply message payload
}
// Implement to retrieve the connectivity state
std::string MyAlexaConnectivityHandler::getConnectivityState();
// Implement to retrieve the identifier
std::string MyAlexaConnectivityHandler::getIdentifier();
};